Note
Click here to download the full example code
07.a stats.2dbin and mpl.heatmap
This script demonstrates how to aggregate 2D data using
scipy.stats.binned_statistic_2d and then visualize the
result as a detailed, annotated heatmap.
It provides a comprehensive workflow that includes:
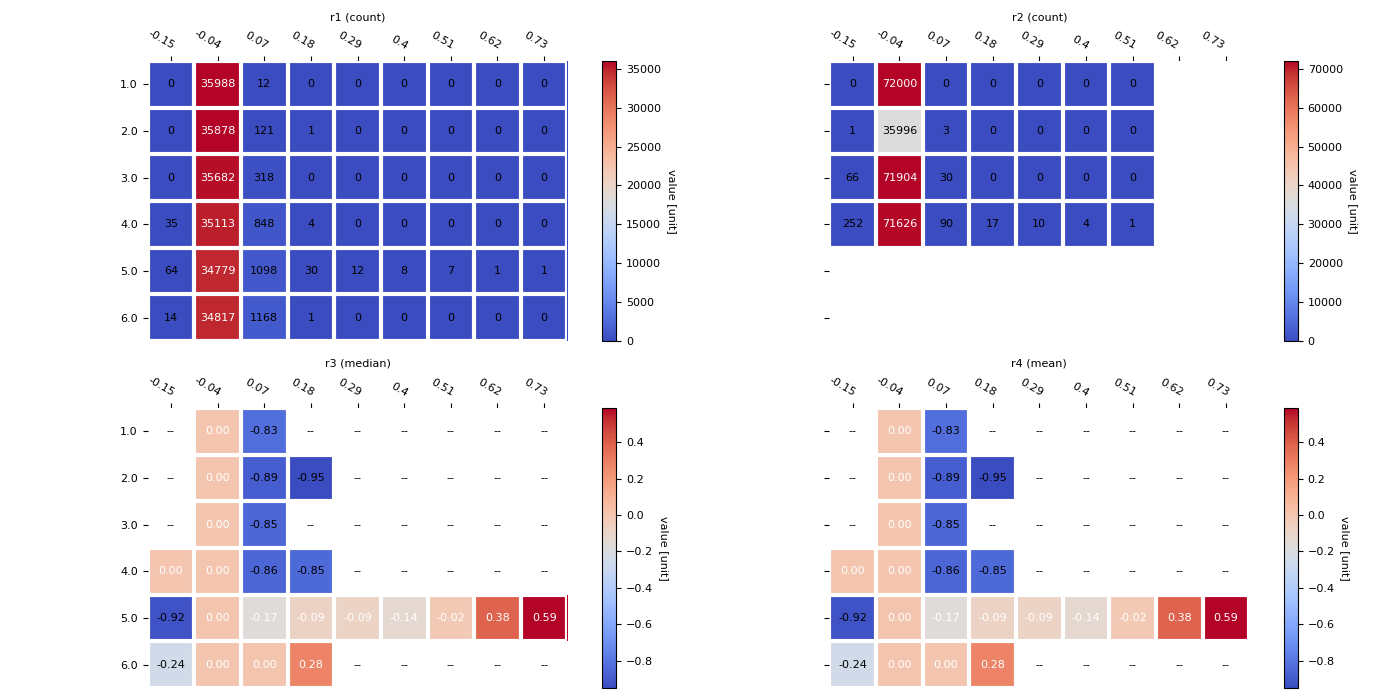
Binning Data: It groups scattered 2D points into a grid and computes statistics like count, median, and mean for the values within each bin.
Custom Heatmap Function: It uses custom helper functions to build a polished heatmap from scratch using
matplotlib, complete with annotations for each cell.
Out:
Unnamed: 0 sample timestep features feature_values shap_values
0 0 0 0 Ward Lactate 0.000000 0.000652
1 1 0 0 Ward Glucose 0.000000 -0.000596
2 2 0 0 Ward sO2 0.000000 0.000231
3 3 0 0 White blood cell count, blood 0.000000 0.000582
4 4 0 0 Platelets 0.000000 -0.001705
... ... ... ... ... ... ...
251995 251995 999 6 Procalcitonin 0.000000 0.000027
251996 251996 999 6 Ferritin 0.000000 -0.001375
251997 251997 999 6 D-Dimer 0.000000 0.000045
251998 251998 999 6 sex -1.000000 -0.002359
251999 251999 999 6 age 0.169952 0.000237
[252000 rows x 6 columns]
C:\Users\kelda\Desktop\repositories\virtualenvs\venv-py311-psc\Lib\site-packages\matplotlib\colors.py:2242: UserWarning:
Warning: converting a masked element to nan.
C:\Users\kelda\Desktop\repositories\virtualenvs\venv-py311-psc\Lib\site-packages\matplotlib\colors.py:2249: UserWarning:
Warning: converting a masked element to nan.
C:\Users\kelda\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python311\Lib\string.py:264: FutureWarning:
Format strings passed to MaskedConstant are ignored, but in future may error or produce different behavior
C:\Users\kelda\Desktop\repositories\virtualenvs\venv-py311-psc\Lib\site-packages\matplotlib\colors.py:2242: UserWarning:
Warning: converting a masked element to nan.
C:\Users\kelda\Desktop\repositories\virtualenvs\venv-py311-psc\Lib\site-packages\matplotlib\colors.py:2249: UserWarning:
Warning: converting a masked element to nan.
C:\Users\kelda\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python311\Lib\string.py:264: FutureWarning:
Format strings passed to MaskedConstant are ignored, but in future may error or produce different behavior
C:\Users\kelda\Desktop\repositories\github\python-spare-code\main\examples\matplotlib\plot_main07_a_2dbin_stat.py:256: UserWarning:
FigureCanvasAgg is non-interactive, and thus cannot be shown
20 import matplotlib
21 import numpy as np
22 import pandas as pd
23 import matplotlib as mpl
24 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
25
26 from scipy import stats
27
28 # See https://matplotlib.org/devdocs/users/explain/customizing.html
29 mpl.rcParams['font.size'] = 8
30 mpl.rcParams['axes.titlesize'] = 8
31 mpl.rcParams['axes.labelsize'] = 8
32 mpl.rcParams['xtick.labelsize'] = 8
33 mpl.rcParams['ytick.labelsize'] = 8
34
35 def heatmap(data, row_labels, col_labels, ax=None,
36 cbar_kw=None, cbarlabel="", **kwargs):
37 """
38 Create a heatmap from a numpy array and two lists of labels.
39
40 Parameters
41 ----------
42 data
43 A 2D numpy array of shape (M, N).
44 row_labels
45 A list or array of length M with the labels for the rows.
46 col_labels
47 A list or array of length N with the labels for the columns.
48 ax
49 A `matplotlib.axes.Axes` instance to which the heatmap is plotted. If
50 not provided, use current axes or create a new one. Optional.
51 cbar_kw
52 A dictionary with arguments to `matplotlib.Figure.colorbar`. Optional.
53 cbarlabel
54 The label for the colorbar. Optional.
55 **kwargs
56 All other arguments are forwarded to `imshow`.
57 """
58
59 if ax is None:
60 ax = plt.gca()
61
62 if cbar_kw is None:
63 cbar_kw = {}
64
65 # Plot the heatmap
66 im = ax.imshow(data, **kwargs)
67
68 # Create colorbar
69 cbar = ax.figure.colorbar(im, ax=ax, **cbar_kw)
70 cbar.ax.set_ylabel(cbarlabel, rotation=-90, va="bottom")
71
72 # Show all ticks and label them with the respective list entries.
73 ax.set_xticks(np.arange(data.shape[1]), labels=col_labels)
74 ax.set_yticks(np.arange(data.shape[0]), labels=row_labels)
75
76 # Let the horizontal axes labeling appear on top.
77 ax.tick_params(top=True, bottom=False,
78 labeltop=True, labelbottom=False)
79
80 # Rotate the tick labels and set their alignment.
81 plt.setp(ax.get_xticklabels(), rotation=-30, ha="right",
82 rotation_mode="anchor")
83
84 # Turn spines off and create white grid.
85 ax.spines[:].set_visible(False)
86
87 ax.set_xticks(np.arange(data.shape[1]+1)-.5, minor=True)
88 ax.set_yticks(np.arange(data.shape[0]+1)-.5, minor=True)
89 ax.grid(which="minor", color="w", linestyle='-', linewidth=3)
90 ax.tick_params(which="minor", bottom=False, left=False)
91
92 return im, cbar
93
94
95 def annotate_heatmap(im, data=None, valfmt="{x:.2f}",
96 textcolors=("black", "white"),
97 threshold=None, **textkw):
98 """
99 A function to annotate a heatmap.
100
101 Parameters
102 ----------
103 im
104 The AxesImage to be labeled.
105 data
106 Data used to annotate. If None, the image's data is used. Optional.
107 valfmt
108 The format of the annotations inside the heatmap. This should either
109 use the string format method, e.g. "$ {x:.2f}", or be a
110 `matplotlib.ticker.Formatter`. Optional.
111 textcolors
112 A pair of colors. The first is used for values below a threshold,
113 the second for those above. Optional.
114 threshold
115 Value in data units according to which the colors from textcolors are
116 applied. If None (the default) uses the middle of the colormap as
117 separation. Optional.
118 **kwargs
119 All other arguments are forwarded to each call to `text` used to create
120 the text labels.
121 """
122
123 if not isinstance(data, (list, np.ndarray)):
124 data = im.get_array()
125
126 # Normalize the threshold to the images color range.
127 if threshold is not None:
128 threshold = im.norm(threshold)
129 else:
130 threshold = im.norm(data.max())/2.
131
132 # Set default alignment to center, but allow it to be
133 # overwritten by textkw.
134 kw = dict(horizontalalignment="center",
135 verticalalignment="center")
136 kw.update(textkw)
137
138 # Get the formatter in case a string is supplied
139 if isinstance(valfmt, str):
140 valfmt = matplotlib.ticker.StrMethodFormatter(valfmt)
141
142 # Loop over the data and create a `Text` for each "pixel".
143 # Change the text's color depending on the data.
144 texts = []
145 for i in range(data.shape[0]):
146 for j in range(data.shape[1]):
147 kw.update(color=textcolors[int(im.norm(data[i, j]) > threshold)])
148 text = im.axes.text(j, i, valfmt(data[i, j], None), **kw)
149 texts.append(text)
150
151 return texts
152
153
154 def plot_binned_statistic(r, ax, title=None, astype=None, **kwargs):
155 """Plots the binned statistic
156
157 Parameters
158 ----------
159 r: the binned statistic
160 ax: the axes to plot
161
162 Returns
163 -------
164 """
165 # Variables
166 rows, cols = r.statistic.shape
167
168 # Compute centers
169 x_center = (r.x_edge[:-1] + r.x_edge[1:]) / 2
170 y_center = (r.y_edge[:-1] + r.y_edge[1:]) / 2
171
172 # Plot heatmap (matplotlib sample, use seaborn instead)
173 im, cbar = heatmap(r.statistic,
174 np.around(x_center, 2), np.around(y_center, 2), ax=ax,
175 cmap="coolwarm", cbarlabel="value [unit]")
176 texts = annotate_heatmap(im, **kwargs)
177
178 # Configure
179 ax.set_aspect('equal', 'box')
180 if title is not None:
181 ax.set_title(title)
182
183 """
184 # Show
185 print("\n\n")
186 print(matrix)
187 print(r.x_edge)
188 print(r.y_edge)
189 print(r.binnumber)
190 print(np.flip(r.statistic, axis=1))
191 """
192
193 def data_manual():
194 """"""
195 # Create random values
196 x = np.array([1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 4])
197 y = np.array([1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
198 z = np.array([1, 9, 9, 1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 4])
199 return x, y, z
200
201 def data_shap():
202 """"""
203 data = pd.read_csv('../../datasets/shap/shap.csv')
204 print(data)
205 return data.timestep, data.shap_values, data.feature_values
206
207
208
209
210 # Load data
211 #x, y, z = data_manual()
212 x, y, z = data_shap()
213
214 # Using np.arange
215 binx = np.arange(0, x.max()+1) + 0.5 # [0.5, 1.5, 2.5, ...., N + 0.5]
216 biny = np.arange(0, y.max()+1) + 0.5 # [0.5, 1.5, 2.5, ...., N + 0.5]
217
218 # Using np.linspace
219 biny = np.linspace(y.min(), y.max(), 10)
220
221 # Manual
222 #binx = np.arange(5) + 0.5
223 #biny = np.arange(8) + 0.5
224
225 # Compute binned statistic (count)
226 r1 = stats.binned_statistic_2d(x=x, y=y, values=None,
227 statistic='count', bins=[binx, biny],
228 expand_binnumbers=True)
229
230 # Compute binned statistic (median)
231 r2 = stats.binned_statistic_2d(x=x, y=y, values=z,
232 statistic='count', bins=[4, 7],
233 expand_binnumbers=False)
234
235 # Compute binned statistic (median)
236 r3 = stats.binned_statistic_2d(x=x, y=y, values=z,
237 statistic='median', bins=[binx, biny],
238 expand_binnumbers=False)
239
240 # Compute binned statistic (median)
241 r4 = stats.binned_statistic_2d(x=x, y=y, values=z,
242 statistic='mean', bins=[binx, biny],
243 expand_binnumbers=False)
244
245
246 # Plot
247 fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2,
248 sharey=True, sharex=True, figsize=(14, 7))
249 plot_binned_statistic(r1, axs[0,0], title='r1 (count)', valfmt="{x:g}")
250 plot_binned_statistic(r2, axs[0,1], title='r2 (count)', valfmt="{x:g}")
251 plot_binned_statistic(r3, axs[1,0], title='r3 (median)')
252 plot_binned_statistic(r3, axs[1,1], title='r4 (mean)')
253
254 # Display
255 plt.tight_layout()
256 plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 1.031 seconds)