Note
Click here to download the full example code
02. Point density with matplotlib.hexbin
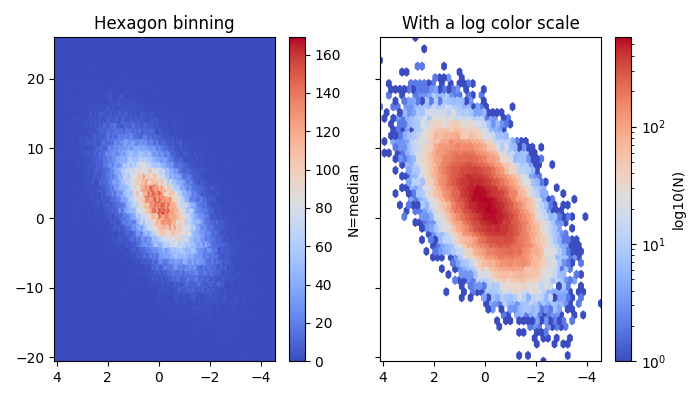
This script demonstrates how to create a 2D hexagonal binning
plot with matplotlib.hexbin. 🐝 This type of plot is an
excellent alternative to a scatter plot for visualizing the
density of a large number of points. The example generates
random data and displays it using both linear and logarithmic
color scales to represent point concentration.
Out:
C:\Users\kelda\Desktop\repositories\github\python-spare-code\main\examples\matplotlib\plot_main02_hexbin.py:59: UserWarning:
FigureCanvasAgg is non-interactive, and thus cannot be shown
14 import pandas as pd
15 import numpy as np
16 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
17
18 # constant
19 n = 100000
20
21 # Fixing random state for reproducibility
22 np.random.seed(19680801)
23
24 # Generate data
25 x = np.random.standard_normal(n)
26 y = 2.0 + 3.0 * x + 4.0 * np.random.standard_normal(n)
27 z = None
28
29 # Compute limits
30 xmin = x.min()
31 xmax = x.max()
32 ymin = y.min()
33 ymax = y.max()
34
35 # Display hexagon binning (linear)
36 fig, axs = plt.subplots(ncols=2, sharey=True, figsize=(7, 4))
37 fig.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.5, left=0.07, right=0.93)
38 ax = axs[0]
39 hb = ax.hexbin(x, y, C=z, cmap='coolwarm', reduce_C_function=np.median)
40 ax.axis([xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax])
41 ax.set_title("Hexagon binning")
42 ax.invert_xaxis()
43 cb = fig.colorbar(hb, ax=ax)
44 cb.set_label('N=median')
45
46 # Display hexagon binning (log)
47 ax = axs[1]
48 hb = ax.hexbin(x, y, C=z, gridsize=50,
49 bins='log', cmap='coolwarm',
50 reduce_C_function=np.median)
51 ax.axis([xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax])
52 ax.set_title("With a log color scale")
53 ax.invert_xaxis()
54 cb = fig.colorbar(hb, ax=ax)
55 cb.set_label('log10(N)')
56
57 # Show
58 plt.tight_layout()
59 plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 1.188 seconds)