Note
Click here to download the full example code
0.4 Visualizing GMM and KDE
This script demonstrates and contrasts two common density estimation techniques on synthetic, clustered data.
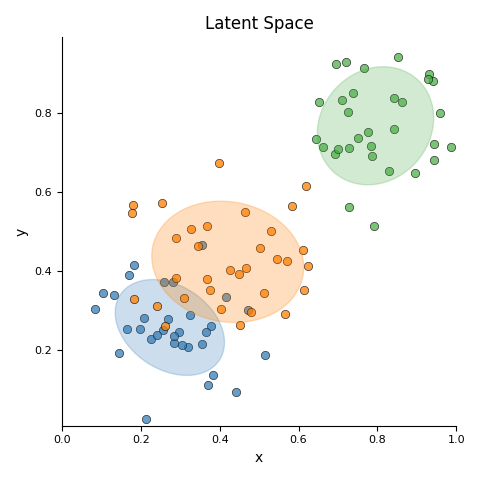
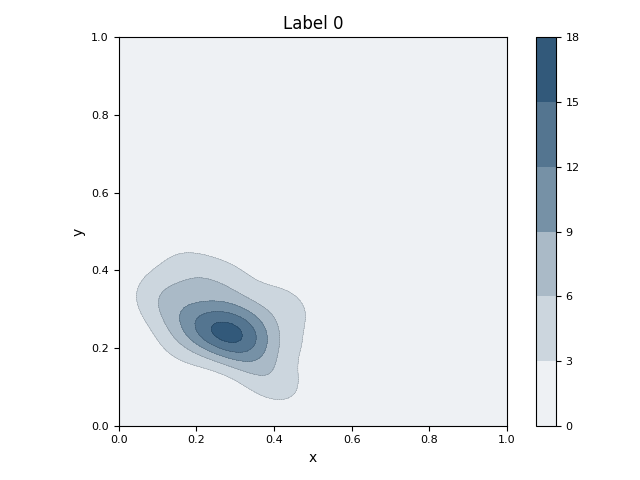
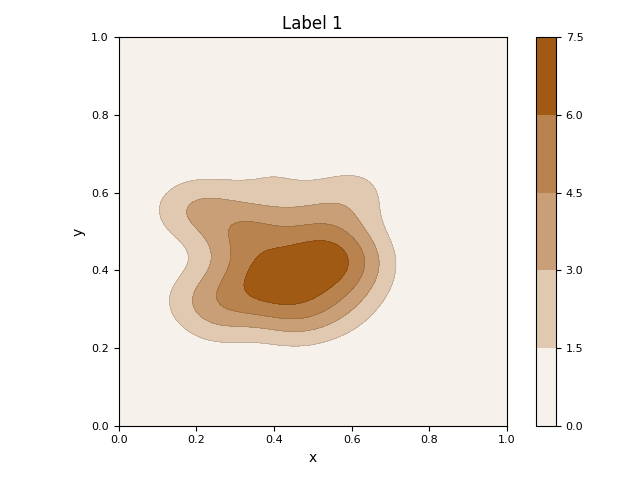
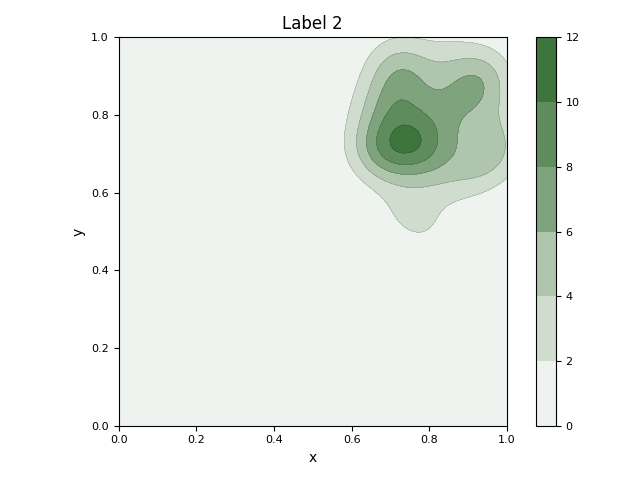
This script first generates a synthetic 2D dataset with three distinct clusters using sklearn.datasets.make_blobs. It then fits a Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) to the entire dataset to parametrically model the underlying distributions of the clusters. The initial visualization displays the raw data points as a scatter plot, with ellipses overlaid to represent the mean and covariance of each learned Gaussian component. Subsequently, the script isolates the data for each class and calculates its non-parametric Kernel Density Estimation (KDE). It generates a separate contour plot for each class, visually representing the probability density of the data points within that specific group.
Out:
Ignoring fixed y limits to fulfill fixed data aspect with adjustable data limits.
C:\Users\kelda\Desktop\repositories\github\python-spare-code\main\examples\matplotlib\plot_main04_gmm_kde.py:334: UserWarning: FigureCanvasAgg is non-interactive, and thus cannot be shown
23 # Libraries
24 import numpy as np
25 import pandas as pd
26 import matplotlib as mpl
27 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
28
29 # Specific
30 from scipy import linalg
31 from sklearn import mixture
32 from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
33 from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
34 from scipy.stats import gaussian_kde
35 from matplotlib.colors import LinearSegmentedColormap
36
37 # Latexify
38 mpl.rc('font', size=10)
39 mpl.rc('legend', fontsize=6)
40 mpl.rc('xtick', labelsize=8)
41 mpl.rc('ytick', labelsize=8)
42
43
44 # -----------------------------------------
45 # Methods
46 # -----------------------------------------
47 def make_colormap(seq):
48 """Return a LinearSegmentedColormap
49
50 Parameters
51 ----------
52 seq: list
53 A sequence of floats and RGB-tuples. The floats
54 should be increasing and in the interval (0,1).
55 """
56 # Library
57 import matplotlib.colors as mcolors
58 # Code
59 seq = [(None,) * 3, 0.0] + list(seq) + [1.0, (None,) * 3]
60 cdict = {'red': [], 'green': [], 'blue': []}
61 for i, item in enumerate(seq):
62 if isinstance(item, float):
63 r1, g1, b1 = seq[i - 1]
64 r2, g2, b2 = seq[i + 1]
65 cdict['red'].append([item, r1, r2])
66 cdict['green'].append([item, g1, g2])
67 cdict['blue'].append([item, b1, b2])
68 return mcolors.LinearSegmentedColormap('CustomMap', cdict)
69
70 def adjust_lightness(color, amount=0.5):
71 """Adjusts the lightness of a color
72
73 Parameters
74 ----------
75 color: string or vector
76 The color in string, hex or rgb format.
77
78 amount: float
79 Lower values result in dark colors.
80 """
81 # Libraries
82 import matplotlib.colors as mc
83 import colorsys
84 try:
85 c = mc.cnames[color]
86 except:
87 c = color
88 c = colorsys.rgb_to_hls(*mc.to_rgb(c))
89 return colorsys.hls_to_rgb(c[0], \
90 max(0, min(1, amount * c[1])), c[2])
91
92 def kde_mpl_compute(x, y, xlim=None, ylim=None, **kwargs):
93 """Computes the gaussian kde.
94
95 Parameters
96 ----------
97
98 Returns
99 -------
100 """
101 try:
102 # Plot density
103 kde = gaussian_kde(np.vstack((x, y)), **kwargs)
104 except Exception as e:
105 print("Exception! %s" % e)
106 return None, None, None
107
108 # Parameters
109 xmin, xmax = min(x), max(x)
110 ymin, ymax = min(y), max(y)
111
112 # Set xlim and ylim
113 if xlim is not None:
114 xmin, xmax = xlim
115 if ylim is not None:
116 ymin, ymax = ylim
117
118 # evaluate on a regular grid
119 xgrid = np.linspace(xmin, xmax, 100)
120 ygrid = np.linspace(ymin, ymax, 100)
121 Xgrid, Ygrid = np.meshgrid(xgrid, ygrid)
122 zgrid = kde.evaluate(np.vstack([
123 Xgrid.ravel(),
124 Ygrid.ravel()
125 ]))
126 Zgrid = zgrid.reshape(Xgrid.shape)
127
128 # Return
129 return xgrid, ygrid, Zgrid
130
131 def plot_ellipses(gmm, ax, color, n=None):
132 """Plot ellipses from GaussianMixtureModel"""
133
134 # Define color
135 if color is None:
136 color = 'blue'
137 if n is None:
138 n = 1
139
140 # Get covariances
141 if gmm.covariance_type == 'full':
142 covariances = gmm.covariances_[n][:2, :2]
143 elif gmm.covariance_type == 'tied':
144 covariances = gmm.covariances_[:2, :2]
145 elif gmm.covariance_type == 'diag':
146 covariances = np.diag(gmm.covariances_[n][:2])
147 elif gmm.covariance_type == 'spherical':
148 covariances = np.eye(gmm.means_.shape[1]) * gmm.covariances_[n]
149
150 # Compute
151 v, w = np.linalg.eigh(covariances)
152 # v = 2. * np.sqrt(2.) * np.sqrt(v) # Oliver
153 u = w[0] / np.linalg.norm(w[0])
154 angle = np.arctan2(u[1], u[0])
155 angle = 180 * angle / np.pi # convert to degrees
156 v = 2. * np.sqrt(2.) * np.sqrt(v)
157
158 # Plot
159 ell = mpl.patches.Ellipse(gmm.means_[n, :2],
160 v[0], v[1], angle=180 + angle, color=color)
161 ell.set_clip_box(ax.bbox)
162 ell.set_alpha(0.25)
163 ax.add_artist(ell)
164 ax.set_aspect('equal', 'datalim')
165
166
167 # -----------------------------------------
168 # Create data
169 # -----------------------------------------
170 # Colors
171 colors = ['#377eb8', '#ff7f00', '#4daf4a',
172 '#a65628', '#984ea3',
173 '#999999', '#e41a1c', '#dede00']
174
175 c1 = colors[0]
176 c2 = colors[1]
177 c3 = colors[2]
178
179 # Data
180 data = [
181 [0.19, 0.25, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
182 [0.15, 0.21, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
183 [0.13, 0.19, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
184 [0.16, 0.12, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
185 [0.21, 0.14, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
186 [0.38, 0.18, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
187
188 [0.50, 0.52, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0],
189 [0.40, 0.58, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0],
190 [0.49, 0.72, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0],
191 [0.44, 0.64, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0],
192 [0.60, 0.50, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0],
193 [0.38, 0.81, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0],
194 [0.40, 0.75, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0],
195 [0.47, 0.61, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0],
196 [0.52, 0.65, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0],
197 [0.50, 0.55, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0],
198 [0.46, 0.54, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0],
199 [0.60, 0.50, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0],
200 [0.68, 0.52, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0],
201 [0.61, 0.77, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0],
202 [0.51, 0.79, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1],
203 [0.64, 0.80, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1],
204 [0.54, 0.75, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1],
205 [0.58, 0.81, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1],
206
207 [0.80, 0.82, 2, 0, 0, 1, 1],
208 [0.85, 0.83, 2, 0, 0, 1, 1],
209 [0.90, 0.85, 2, 0, 0, 1, 1],
210 [0.84, 0.80, 2, 0, 0, 1, 1],
211 [0.81, 0.78, 2, 0, 0, 1, 1],
212 [0.92, 0.79, 2, 0, 0, 1, 1],
213 ]
214
215 """
216 # Create DataFrame (manual data)
217 data = pd.DataFrame(data)
218 data.columns = ['x', 'y', 'target',
219 'Label 0', 'Label 1', 'Label 2',
220 'Label 3']
221 """
222
223 # Create bloobs
224 X, y = make_blobs(n_features=2,
225 centers=[[0.35, 0.35],
226 [0.45, 0.45],
227 [0.7, 0.70]],
228 cluster_std=[0.07, 0.10, 0.07])
229
230 # Preprocessing
231 X = MinMaxScaler().fit_transform(X)
232
233 # Create Dataframe
234 data = pd.DataFrame(X, columns=['x', 'y'])
235 data['target'] = y
236 for i in np.unique(y):
237 data['Label %s' % i] = y==i
238 data = data[(data.x>0) & (data.x<1)]
239 data = data[(data.y>0) & (data.y<1)]
240
241 # Create X
242 X = data[['x', 'y']]
243
244 # Create gaussian
245 gmm = mixture.GaussianMixture(
246 n_components=3, covariance_type='full')
247
248 # Since we have class labels for the training data, we can
249 # initialize the GMM parameters in a supervised manner.
250 gmm.means_init = np.array( \
251 [X[data.target == i].mean(axis=0)
252 for i in range(3)])
253
254 # Fit a Gaussian mixture with EM using five components
255 gmm = gmm.fit(data[['x', 'y']])
256
257
258 # -----------------------------------------
259 # Visualisation (
260 # -----------------------------------------
261 # Create figure
262 figure, ax = plt.subplots(1,1, figsize=(4.8, 4.8))
263
264 for i, (c, aux) in enumerate(data.groupby('target')):
265
266 # Plot markers
267 ax.scatter(aux.x, aux.y, c=colors[i],
268 edgecolors='k', alpha=0.75,
269 linewidths=0.5)
270
271 # Plot ellipse
272 plot_ellipses(gmm, ax, color=colors[i], n=i)
273
274 # Configure
275 ax.set(xlabel='x', ylabel='y',
276 aspect='equal',
277 xlim=[0, 1], ylim=[0, 1],
278 title='Latent Space')
279
280 # Hide the right and top spines
281 ax.spines.right.set_visible(False)
282 ax.spines.top.set_visible(False)
283
284 # Adjust
285 plt.tight_layout()
286
287
288 # -----------------------------------------
289 # Visualisation labels
290 # -----------------------------------------
291 # Loop
292 for i, l in enumerate(['Label 0',
293 'Label 1',
294 'Label 2']):
295 # Filter data
296 aux = data[data[l] == 1]
297
298 # Compute KDE
299 xgrid, ygrid, Zgrid = \
300 kde_mpl_compute(aux.x, aux.y,
301 xlim=[0, 1], ylim=[0, 1])
302
303 # Create colormap
304 cmap = LinearSegmentedColormap.from_list("",
305 ['white', adjust_lightness(colors[i], 0.6)], 14)
306
307 # Create figure
308 figure, ax = plt.subplots(1,1)
309
310 # Plot contour
311 ax.contour(xgrid, ygrid, Zgrid,
312 linewidths=0.25, alpha=0.5, levels=5,
313 linestyles='dashed', colors='k')
314 # Plot fill spaces
315 cntr = ax.contourf(xgrid, ygrid, Zgrid,
316 levels=5, cmap=cmap)
317 # Add colorbar
318 cb = plt.colorbar(cntr, ax=ax)
319
320 # Configure
321 ax.set(xlabel='x', ylabel='y',
322 aspect='equal', title=l,
323 xlim=[0, 1], ylim=[0, 1])
324
325 # Adjust
326 plt.tight_layout()
327
328
329 # -----------------------------------------
330 # All together
331 # -----------------------------------------
332
333 # Con
334 plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 2.953 seconds)