Note
Click here to download the full example code
05a. Custom using stripplot
This script demonstrates how to create a custom visualization for
sequential or time-series SHAP values using seaborn.stripplot.
This approach provides a granular, per-feature view of how SHAP
values are distributed across different timesteps, offering an
alternative to the standard SHAP library plots.
The script’s workflow focuses on:
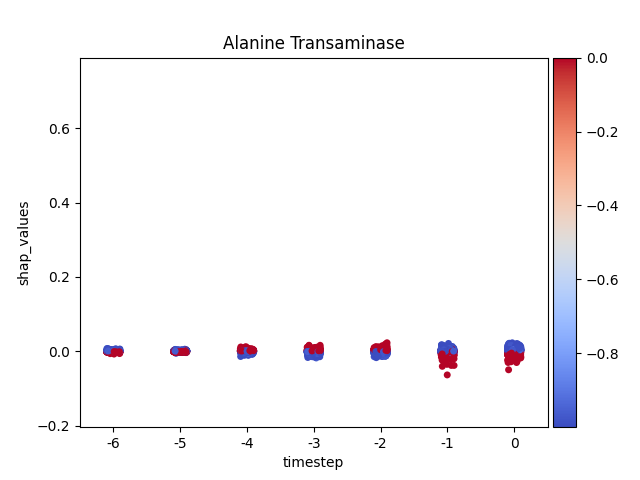
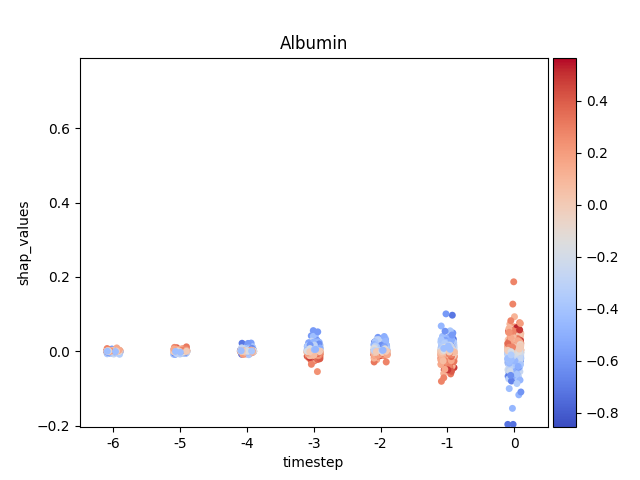
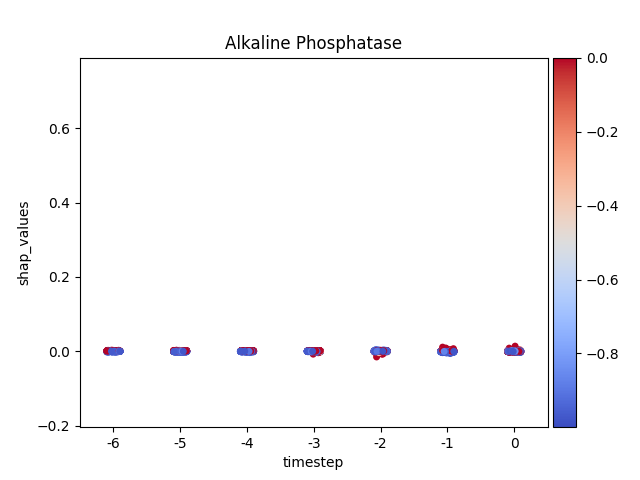
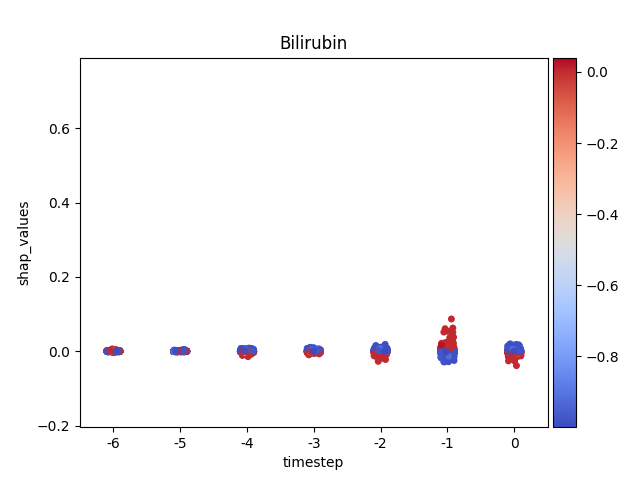
Loading Pre-computed Data: It ingests a tidy DataFrame of SHAP and feature values, structured for time-series analysis.
**Per-Feature Visualization:*8 It iterates through each feature, generating a dedicated stripplot to isolate its impact over time without the influence of other features.
Advanced Coloring: A key feature is the custom implementation of coloring each data point by its original feature value, complete with a color bar, to replicate the rich context provided in native SHAP plots.
8Plot Customization:* It shows how to control axes, legends, and other plot aesthetics for a polished final visualization.
While noted to be slower than other methods, this example is ideal for creating detailed, publication-quality plots that reveal the dynamics of feature contributions over a sequence.
30 # Libraries
31 import shap
32 import numpy as np
33 import pandas as pd
34 import seaborn as sns
35
36 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
37 import matplotlib as mpl
38 import matplotlib.colorbar
39 import matplotlib.colors
40 import matplotlib.cm
41
42 from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1 import make_axes_locatable
43
44 try:
45 __file__
46 TERMINAL = True
47 except:
48 TERMINAL = False
49
50
51 # ------------------------
52 # Methods
53 # ------------------------
54 def scalar_colormap(values, cmap, vmin, vmax):
55 """This method creates a colormap based on values.
56
57 Parameters
58 ----------
59 values : array-like
60 The values to create the corresponding colors
61
62 cmap : str
63 The colormap
64
65 vmin, vmax : float
66 The minimum and maximum possible values
67
68 Returns
69 -------
70 scalar colormap
71 """
72 # Create scalar mappable
73 norm = mpl.colors.Normalize(vmin=vmin, vmax=vmax, clip=True)
74 mapper = mpl.cm.ScalarMappable(norm=norm, cmap=cmap)
75 # Get color map
76 colormap = sns.color_palette([mapper.to_rgba(i) for i in values])
77 # Return
78 return colormap, norm
79
80
81 def scalar_palette(values, cmap, vmin, vmax):
82 """This method creates a colorpalette based on values.
83
84 Parameters
85 ----------
86 values : array-like
87 The values to create the corresponding colors
88
89 cmap : str
90 The colormap
91
92 vmin, vmax : float
93 The minimum and maximum possible values
94
95 Returns
96 -------
97 scalar colormap
98
99 """
100 # Create a matplotlib colormap from name
101 # cmap = sns.light_palette(cmap, reverse=False, as_cmap=True)
102 cmap = sns.color_palette(cmap, as_cmap=True)
103 # Normalize to the range of possible values from df["c"]
104 norm = mpl.colors.Normalize(vmin=vmin, vmax=vmax)
105 # Create a color dictionary (value in c : color from colormap)
106 colors = {}
107 for cval in values:
108 colors.update({cval: cmap(norm(cval))})
109 # Return
110 return colors, norm
111
112
113 def load_shap_file():
114 """Load shap file.
115
116 .. note: The timestep does not indicate time step but matrix
117 index index. Since the matrix index for time steps
118 started in negative t=-T and ended in t=0 the
119 transformation should be taken into account.
120
121 """
122 from pathlib import Path
123 # Load data
124 path = Path('../../datasets/shap/')
125 data = pd.read_csv(path / 'shap.csv')
126 data = data.iloc[:, 1:]
127 data = data.rename(columns={'timestep': 'indice'})
128 data['timestep'] = data.indice - (data.indice.nunique() - 1)
129 return data
130
131
132
133 # -------------------------------------------------------------------
134 # Main
135 # -------------------------------------------------------------------
136 # Configuration
137 cmap_name = 'coolwarm' # colormap name
138 norm_shap = True
139
140 # Load data
141 data = load_shap_file()
142 #data = data[data['sample'] < 100]
143
144 # Show
145 if TERMINAL:
146 print("\nShow:")
147 print(data)
Let’s see how data looks like
151 data.head(10)
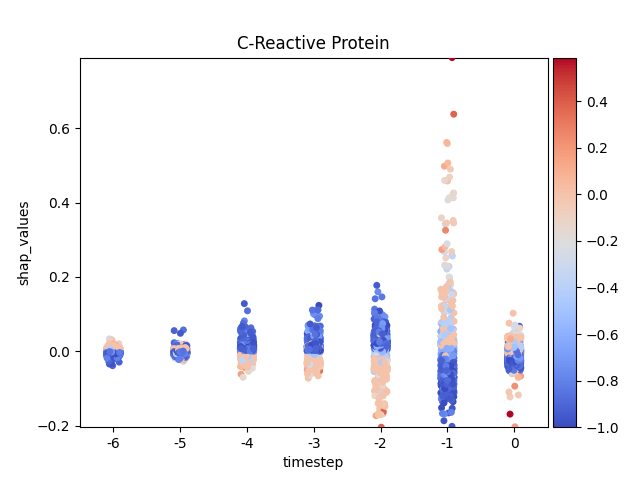
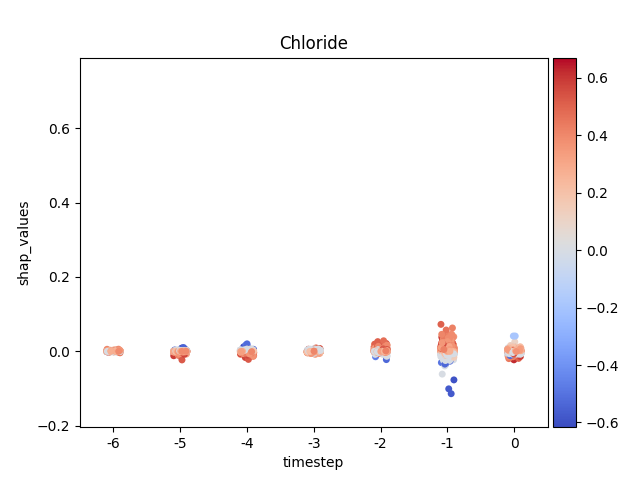
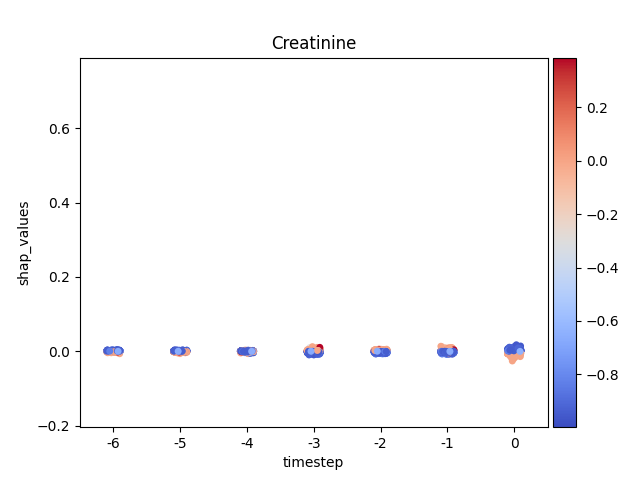
Let’s show using sns.stripplot
Warning
This method seems to be quite slow.
Note
y-axis has been ‘normalized’
162 def add_colorbar(fig, cmap, norm):
163 """"""
164 divider = make_axes_locatable(plt.gca())
165 ax_cb = divider.new_horizontal(size="5%", pad=0.05)
166 fig.add_axes(ax_cb)
167 cb1 = matplotlib.colorbar.ColorbarBase(ax_cb,
168 cmap=cmap, norm=norm, orientation='vertical')
169
170
171 # Loop
172 for i, (name, df) in enumerate(data.groupby('features')):
173
174 # Get colormap
175 values = df.feature_values
176 cmap, norm = scalar_palette(values=values,
177 cmap=cmap_name, vmin=values.min(),
178 vmax=values.max())
179
180 # Display
181 fig, ax = plt.subplots()
182 ax = sns.stripplot(x='timestep',
183 y='shap_values',
184 hue='feature_values',
185 palette=cmap,
186 data=df,
187 ax=ax)
188
189 # Format figure
190 plt.title(name)
191 plt.legend([], [], frameon=False)
192
193 if norm_shap:
194 plt.ylim(data.shap_values.min(),
195 data.shap_values.max())
196
197 # Invert x axis (if no negative timesteps)
198 #ax.invert_xaxis()
199
200 # Create colormap (fix for old versions of mpl)
201 cmap = matplotlib.cm.get_cmap(cmap_name)
202
203 # Add colorbar
204 add_colorbar(plt.gcf(), cmap, norm)
205
206 # Show only first N
207 if int(i) > 5:
208 break
209
210 # Show
211 plt.show()
Out:
C:\Users\kelda\Desktop\repositories\github\python-spare-code\main\examples\shap\plot_main05_stripplot.py:201: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning:
The get_cmap function was deprecated in Matplotlib 3.7 and will be removed in 3.11. Use ``matplotlib.colormaps[name]`` or ``matplotlib.colormaps.get_cmap()`` or ``pyplot.get_cmap()`` instead.
C:\Users\kelda\Desktop\repositories\github\python-spare-code\main\examples\shap\plot_main05_stripplot.py:201: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning:
The get_cmap function was deprecated in Matplotlib 3.7 and will be removed in 3.11. Use ``matplotlib.colormaps[name]`` or ``matplotlib.colormaps.get_cmap()`` or ``pyplot.get_cmap()`` instead.
C:\Users\kelda\Desktop\repositories\github\python-spare-code\main\examples\shap\plot_main05_stripplot.py:201: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning:
The get_cmap function was deprecated in Matplotlib 3.7 and will be removed in 3.11. Use ``matplotlib.colormaps[name]`` or ``matplotlib.colormaps.get_cmap()`` or ``pyplot.get_cmap()`` instead.
C:\Users\kelda\Desktop\repositories\github\python-spare-code\main\examples\shap\plot_main05_stripplot.py:201: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning:
The get_cmap function was deprecated in Matplotlib 3.7 and will be removed in 3.11. Use ``matplotlib.colormaps[name]`` or ``matplotlib.colormaps.get_cmap()`` or ``pyplot.get_cmap()`` instead.
C:\Users\kelda\Desktop\repositories\github\python-spare-code\main\examples\shap\plot_main05_stripplot.py:201: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning:
The get_cmap function was deprecated in Matplotlib 3.7 and will be removed in 3.11. Use ``matplotlib.colormaps[name]`` or ``matplotlib.colormaps.get_cmap()`` or ``pyplot.get_cmap()`` instead.
C:\Users\kelda\Desktop\repositories\github\python-spare-code\main\examples\shap\plot_main05_stripplot.py:201: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning:
The get_cmap function was deprecated in Matplotlib 3.7 and will be removed in 3.11. Use ``matplotlib.colormaps[name]`` or ``matplotlib.colormaps.get_cmap()`` or ``pyplot.get_cmap()`` instead.
C:\Users\kelda\Desktop\repositories\github\python-spare-code\main\examples\shap\plot_main05_stripplot.py:201: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning:
The get_cmap function was deprecated in Matplotlib 3.7 and will be removed in 3.11. Use ``matplotlib.colormaps[name]`` or ``matplotlib.colormaps.get_cmap()`` or ``pyplot.get_cmap()`` instead.
C:\Users\kelda\Desktop\repositories\github\python-spare-code\main\examples\shap\plot_main05_stripplot.py:211: UserWarning:
FigureCanvasAgg is non-interactive, and thus cannot be shown
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 8.549 seconds)