Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Using autoregressive model ARIMA
Approximate a function using Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA)
Series:
arima-aic 787.9221
arima-bic 795.0681
arima-hqic 790.7871
arima-llf -390.961
arima-const_coef 295.273
arima-const_std 112.5006
arima-const_tvalue 2.6246
arima-const_tprob 0.0087
arima-const_cil 74.7759
arima-const_ciu 515.77
arima-ar.L1_coef 0.9829
arima-ar.L1_std 0.0218
arima-ar.L1_tvalue 45.0214
arima-ar.L1_tprob 0.0
arima-ar.L1_cil 0.9401
arima-ar.L1_ciu 1.0257
arima-sigma2_coef 986.1961
arima-sigma2_std 151.4148
arima-sigma2_tvalue 6.5132
arima-sigma2_tprob 0.0
arima-sigma2_cil 689.4286
arima-sigma2_ciu 1282.9636
arima-m_dw 1.9881
arima-m_jb_value 674.0007
arima-m_jb_prob 0.0
arima-m_skew -2.686
arima-m_kurtosis 16.166
arima-m_nm_value 73.4145
arima-m_nm_prob 0.0
arima-m_ks_value 0.549
arima-m_ks_prob 0.0
arima-m_shp_value 0.7978
arima-m_shp_prob 0.0
arima-m_ad_value 2.1004
arima-m_ad_nnorm False
arima-converged True
arima-endog [59.839700...
arima-order (1, 0, 0)
arima-trend c
arima-disp 0
arima-model <statsmode...
arima-id ARIMA(1, 0...
dtype: object
Summary:
SARIMAX Results
==============================================================================
Dep. Variable: y No. Observations: 80
Model: ARIMA(1, 0, 0) Log Likelihood -390.961
Date: Thu, 15 Jun 2023 AIC 787.922
Time: 18:15:49 BIC 795.068
Sample: 0 HQIC 790.787
- 80
Covariance Type: opg
==============================================================================
coef std err z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
const 295.2730 112.501 2.625 0.009 74.776 515.770
ar.L1 0.9829 0.022 45.021 0.000 0.940 1.026
sigma2 986.1961 151.415 6.513 0.000 689.429 1282.964
==============================================================================
Manual
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Omnibus: 0.000 Durbin-Watson: 1.988
Prob(Omnibus): 0.000 Jarque-Bera (JB): 674.001
Skew: -2.686 Prob(JB): 0.000
Kurtosis_m: 16.166 Cond No:
Normal (N): 73.415 Prob(N): 0.000
==============================================================================
9 # Import.
10 import sys
11 import warnings
12 import pandas as pd
13 import matplotlib as mpl
14 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
15
16 # Import ARIMA from statsmodels.
17 #from statsmodels.tsa.arima_model import ARIMA
18 from statsmodels.tsa.arima.model import ARIMA
19
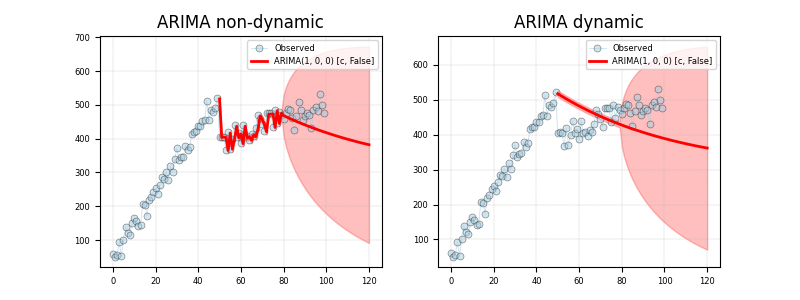
20 # import weights.
21 from pyamr.datasets.load import make_timeseries
22 from pyamr.core.regression.arima import ARIMAWrapper
23
24 # Filter warnings
25 warnings.simplefilter(action='ignore', category=FutureWarning)
26
27 # ----------------------------
28 # set basic configuration
29 # ----------------------------
30 # Matplotlib options
31 mpl.rc('legend', fontsize=6)
32 mpl.rc('xtick', labelsize=6)
33 mpl.rc('ytick', labelsize=6)
34
35 # Set pandas configuration.
36 pd.set_option('display.max_colwidth', 14)
37 pd.set_option('display.width', 150)
38 pd.set_option('display.precision', 4)
39
40 # ----------------------------
41 # create data
42 # ----------------------------
43 # Create timeseries data
44 x, y, f = make_timeseries()
45
46 # Create exogenous variable
47 exog = x
48
49 # ----------------------------
50 # fit the model
51 # ----------------------------
52 # Create specific arima model.
53 arima = ARIMAWrapper(estimator=ARIMA).fit( \
54 endog=y[:80], order=(1,0,0), trend='c', disp=0)
55
56 # Print series
57 print("\nSeries:")
58 print(arima.as_series())
59
60 # Print summary.
61 print("\nSummary:")
62 print(arima.as_summary())
63
64 # -----------------
65 # Save & Load
66 # -----------------
67 # File location
68 #fname = '../../examples/saved/arima-sample.pickle'
69
70 # Save
71 #arima.save(fname=fname)
72
73 # Load
74 #arima = ARIMAWrapper().load(fname=fname)
75
76
77 # -----------------
78 # Predict and plot
79 # -----------------
80 # This example shows how to make predictions using the wrapper which has
81 # been previously fitted. It also demonstrateds how to plot the resulting
82 # data for visualization purposes. It shows two different types of
83 # predictions:
84 # - dynamic predictions in which the prediction is done based on the
85 # previously predicted values. Note that for the case of ARIMA(0,1,1)
86 # it returns a line.
87 # - not dynamic in which the prediction is done based on the real
88 # values of the time series, no matter what the prediction was for
89 # those values.
90
91 # Variables.
92 s, e = 50, 120
93
94 # Compute predictions
95 preds_1 = arima.get_prediction(start=s, end=e, dynamic=False)
96 preds_2 = arima.get_prediction(start=s, end=e, dynamic=True)
97
98 # Create figure
99 fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(8,3))
100
101 # ----------------
102 # Plot non-dynamic
103 # ----------------
104 # Plot truth values.
105 axes[0].plot(y, color='#A6CEE3', alpha=0.5, marker='o',
106 markeredgecolor='k', markeredgewidth=0.5,
107 markersize=5, linewidth=0.75, label='Observed')
108
109 # Plot forecasted values.
110 axes[0].plot(preds_1[0,:], preds_1[1,:], color='#FF0000', alpha=1.00,
111 linewidth=2.0, label=arima._identifier())
112
113 # Plot the confidence intervals.
114 axes[0].fill_between(preds_1[0,:], preds_1[2,:],
115 preds_1[3,:],
116 color='#FF0000',
117 alpha=0.25)
118
119 # ------------
120 # Plot dynamic
121 # ------------
122 # Plot truth values.
123 axes[1].plot(y, color='#A6CEE3', alpha=0.5, marker='o',
124 markeredgecolor='k', markeredgewidth=0.5,
125 markersize=5, linewidth=0.75, label='Observed')
126
127 # Plot forecasted values.
128 axes[1].plot(preds_2[0,:], preds_2[1,:], color='#FF0000', alpha=1.00,
129 linewidth=2.0, label=arima._identifier())
130
131 # Plot the confidence intervals.
132 axes[1].fill_between(preds_2[0,:], preds_2[2,:],
133 preds_2[3,:],
134 color='#FF0000',
135 alpha=0.25)
136
137 # Configure axes
138 axes[0].set_title("ARIMA non-dynamic")
139 axes[1].set_title("ARIMA dynamic")
140
141 # Format axes
142 axes[0].grid(True, linestyle='--', linewidth=0.25)
143 axes[1].grid(True, linestyle='--', linewidth=0.25)
144
145 # Legend
146 axes[0].legend()
147 axes[1].legend()
148
149 # Show
150 plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.175 seconds)