Note
Click here to download the full example code
06. Threshold moving approaches
Out:
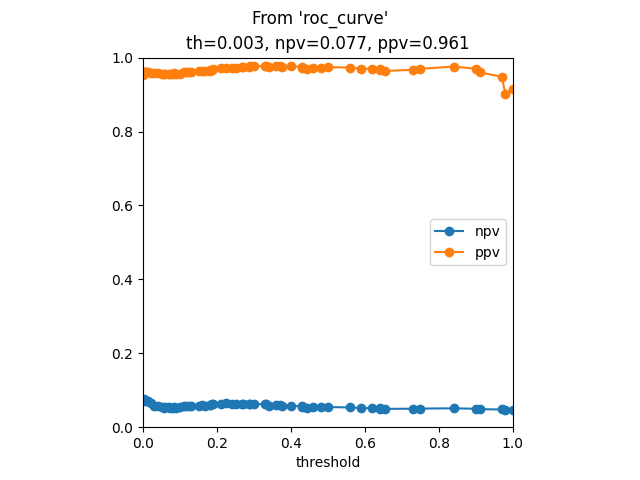
Results from 'roc_curve'
th ppv npv sens spec gmean
69 0.000 0.951872 NaN 1.000000 0.000000 0.000000
68 0.010 0.961945 0.085375 0.795455 0.377622 0.256511
67 0.015 0.962139 0.081454 0.772727 0.398601 0.296193
66 0.020 0.963411 0.085375 0.772727 0.419580 0.295118
65 0.030 0.963836 0.086675 0.772727 0.426573 0.292956
.. ... ... ... ... ... ...
4 0.970 0.969824 0.049887 0.090909 0.944056 0.574130
3 0.980 0.977196 0.050589 0.090909 0.958042 0.569404
2 0.990 0.980924 0.050939 0.090909 0.965035 0.554987
1 1.000 0.974726 0.049759 0.068182 0.965035 0.548071
0 inf NaN 0.048128 0.000000 1.000000 0.000000
[70 rows x 6 columns]
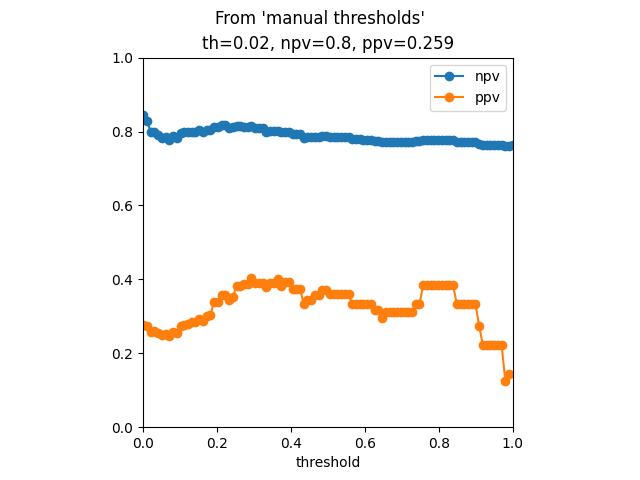
Results from manual
th ppv npv sens spec
0 0.000000 0.282258 0.857143 0.795455 0.377622
1 0.010101 0.283333 0.850746 0.772727 0.398601
2 0.020202 0.293103 0.859155 0.772727 0.426573
3 0.030303 0.303571 0.866667 0.772727 0.454545
4 0.040404 0.305556 0.860759 0.750000 0.475524
.. ... ... ... ... ...
95 0.959596 0.333333 0.771429 0.090909 0.944056
96 0.969697 0.333333 0.771429 0.090909 0.944056
97 0.979798 0.400000 0.774011 0.090909 0.958042
98 0.989899 0.444444 0.775281 0.090909 0.965035
99 1.000000 NaN 0.764706 0.000000 1.000000
[100 rows x 5 columns]
8 # Libraries
9 import numpy as np
10 import pandas as pd
11 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
12
13 # Libraries scikits
14 from sklearn.datasets import fetch_openml
15 from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
16 from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer
17 from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
18 from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
19 from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
20 from sklearn.ensemble import ExtraTreesClassifier
21 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
22
23
24 def display_npv_ppv_curve(ppv, npv, ths, idx):
25 """This method plots the curve
26
27 Parameters
28 ----------
29 ppv: array-like
30 npv: array-like
31 ths: array-like
32 idx: integer
33 """
34 # Display
35 f, axes = plt.subplots(1, 1)
36 axes.plot(ths, npv, marker='o', label='npv')
37 axes.plot(ths, ppv, marker='o', label='ppv')
38 axes.set(aspect='equal', xlim=[0,1], ylim=[0,1],
39 xlabel='threshold', title='th={0}, npv={1}, ppv={2}' \
40 .format(round(ths[idx], 3),
41 round(npv[idx], 3),
42 round(ppv[idx], 3)))
43 plt.legend()
44
45
46 def npv_ppv_from_sens_spec(sens, spec, prev):
47 """Compute npv and ppv.
48
49 Parameters
50 ----------
51 sens: array-like
52 spec: array-like
53 prev: float
54 """
55 npv = (spec * (1 - prev)) / ((spec * (1 - prev)) + ((1 - sens) * prev))
56 ppv = (sens * prev) / ((sens * prev) + ((1 - spec) * (1 - prev)))
57 return npv, ppv
58
59
60
61 # ----------------------
62 # Load data
63 # ----------------------
64 # Fetch data
65 X, y = fetch_openml(data_id=1464,
66 return_X_y=True,
67 as_frame=True)
68 #parser='auto')
69
70 # Format y to binary (0,1)
71 y = y.cat.rename_categories({'1':0, '2':1})
72
73
74 # Split
75 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = \
76 train_test_split(X, y, stratify=y)
77
78 # ----------------------
79 # Create pipeline
80 # ----------------------
81 # Create pipeline
82 clf = make_pipeline(
83 StandardScaler(),
84 #LogisticRegression(random_state=0)
85 ExtraTreesClassifier(n_estimators=100)
86 )
87
88 # Train
89 clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
90
91 # Predictions
92 y_pred = clf.predict(X_test)
93 y_prob = clf.predict_proba(X_test)
94
95 # .. note: Some classifiers do not have the decision
96 # function method but all implement the
97 # predict_proba.
98 #y_score = clf.decision_function(X_test)
99
100 # -----------------------
101 # Show confusion matrix
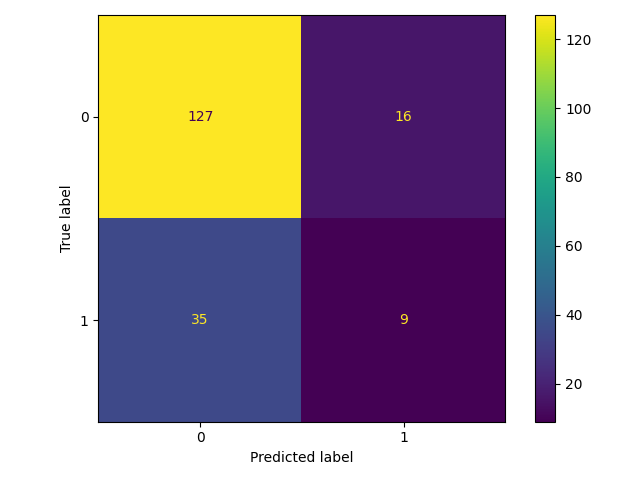
102 # -----------------------
103 # .. note: We are using Display objects to plot
104 # the graphs, they could also be displayed
105 # using the functions or matplotlib
106 # directly.
107 #
108 # plot_roc_curve(clf, X_test, y_test, ax=ax_roc, name=name)
109 # plot_det_curve(clf, X_test, y_test, ax=ax_roc, name=name)
110
111 # Libraries
112 from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
113 from sklearn.metrics import ConfusionMatrixDisplay
114 from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve
115 from sklearn.metrics import RocCurveDisplay
116 from sklearn.metrics import precision_recall_curve
117 from sklearn.metrics import PrecisionRecallDisplay
118
119 # Value counts
120 value_counts = y.value_counts()
121
122 # Prevalence
123 prev = value_counts[1] / len(y_test)
124
125 # Confusion matrix
126 cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
127
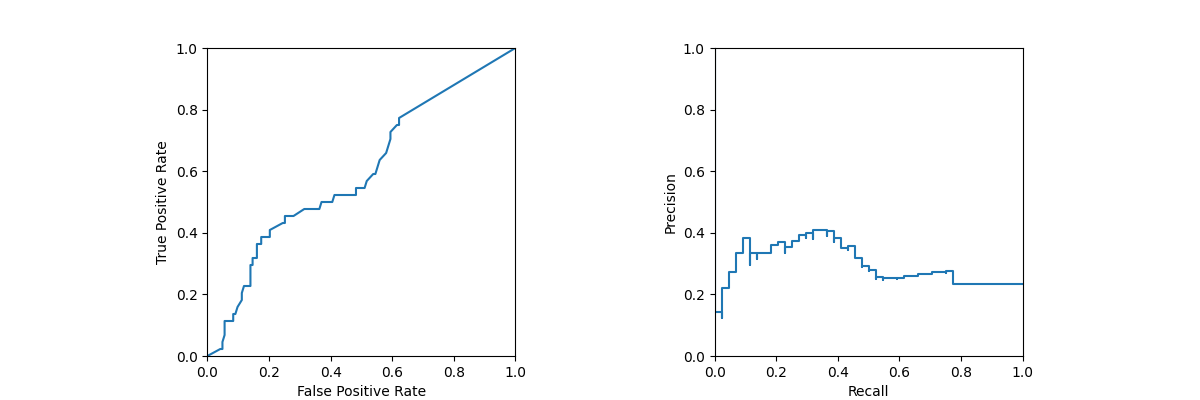
128 # .. note: It is possible to use either y_score
129 # or y_prob in the roc_curve function
130 # .. note: sens=tpr, spec=1-fpr
131 # Compute ROC curve
132 fpr, tpr, ths1 = roc_curve(
133 y_test, y_prob[:, 1],
134 drop_intermediate=False)
135
136 # .. note: ppv=prec, sens=recall
137 # Compute PR curve
138 prec, recall, ths2 = \
139 precision_recall_curve(y_test, y_prob[:, 1])
140
141 # Create plot objects
142 cm_display = ConfusionMatrixDisplay(cm)
143 roc_display = RocCurveDisplay(fpr=fpr, tpr=tpr)
144 pr_display = PrecisionRecallDisplay(precision=prec, recall=recall)
145
146 # Create figure
147 f, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 4))
148 axes = axes.flatten()
149
150 # Display
151 cm_display.plot()
152 roc_display.plot(ax=axes[0])
153 pr_display.plot(ax=axes[1])
154
155 # Configure
156 for ax in axes:
157 ax.set(aspect='equal', xlim=[0,1], ylim=[0,1])
158 plt.tight_layout()
159
160
161
162 # ---------
163 # Option I
164 # ---------
165 # Compute the npv and ppv from the sensitivity
166 # and specificity values obtained from the
167 # 'roc_curve' function.
168
169 # Compute ROC curve
170 fpr, tpr, ths1 = roc_curve(
171 y_test, y_prob[:, 1],
172 drop_intermediate=False)
173
174 # Compute npv and ppv
175 npv, ppv = npv_ppv_from_sens_spec( \
176 sens=tpr, spec=1-fpr, prev=prev)
177
178 # Create DataFrame
179 results = pd.DataFrame(
180 data=np.array([ths1, ppv, npv, tpr, 1-fpr]).T,
181 columns=['th', 'ppv', 'npv', 'sens', 'spec']
182 ).sort_values(by='th')
183
184 # Add gmean
185 results['gmean'] = np.sqrt(tpr * (1-fpr))
186
187 # Find closest to 0.8
188 idx = np.nanargmin(np.abs(npv - 0.8))
189
190 # Find best gmean
191 idx2 = np.argmax(results.gmean)
192
193 # Display
194 display_npv_ppv_curve(ppv, npv, ths1, idx)
195
196 # Title
197 plt.suptitle("From 'roc_curve'")
198
199 # Show
200 print("\n\nResults from 'roc_curve'")
201 print(results)
202
203 """
204 # ---------
205 # Option II
206 # ---------
207 # NOT WORKING!
208 #
209 # Compute the npv by knowing that it is the inverse
210 # of the precision, thus calling the function
211 # 'precision_recall_curve' with opposite labels and
212 # probabilities.
213
214 # .. note: invprec=npv
215 # .. note: invrec=fnr
216 # Computed inverted PR curve
217 invprec, invrec, invths2 = \
218 precision_recall_curve(y_test, y_prob[:, 0],
219 pos_label=clf.classes_[0])
220
221 # Create DataFrame
222 results = pd.DataFrame()
223 results['th'] = invths2[::-1]
224 results['npv'] = invprec[1:]
225 results['ppv'] = 0.0
226 results = results.sort_values(by='th')
227
228 # Find closest to 0.8
229 idx = np.nanargmin(np.abs(invprec - 0.8))
230
231 # Show
232 print("\n\nResults from 'precision_recall_curve'")
233 print(results)
234 print("\nIndex: {0} | Threshold: {1} | NPV: {2}" \
235 .format(idx, invths2[idx-1], npv[idx]))
236
237 # Display graph
238 display_npv_ppv_curve(
239 results.ppv,
240 results.npv,
241 results.th,
242 idx)
243
244 # Title
245 plt.suptitle("From 'precision_recall_curve'")
246 """
247
248 # ----------
249 # Option II
250 # ----------
251 # Perform the computation of metrics and the threshold
252 # search based on a condition (e.g. npv closest to an
253 # specific value) manually.
254 # Thresholds
255 thresholds = np.linspace(0,1,100)
256
257 # Metrics
258 def metrics(y_test, y_prob, th, **kwargs):
259 # Libraries
260 from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
261 # Compute confusion matrix
262 cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_prob>th)
263 tn, fp, fn, tp = cm.ravel()
264 # Compute metrics
265 return {'th': th,
266 'ppv': tp/(tp+fp),
267 'npv': tn/(tn+fn),
268 'sens': tp/(tp+fn),
269 'spec': tn/(tn+fp)}
270
271 # Compute scores
272 scores = [metrics(y_test, y_prob[:,1], t) \
273 for t in thresholds]
274
275 # Create DataFrame
276 results = pd.DataFrame(scores)
277
278 # Find idx where npv is closest to 0.8
279 idx = np.nanargmin(np.abs(results.npv - 0.8))
280
281 # Show
282 print("\n\nResults from manual")
283 print(results)
284
285 # Display graph
286 display_npv_ppv_curve(
287 results.ppv,
288 results.npv,
289 results.th,
290 idx)
291
292 # Title
293 plt.suptitle("From 'manual thresholds'")
294
295 # Show
296 plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.506 seconds)